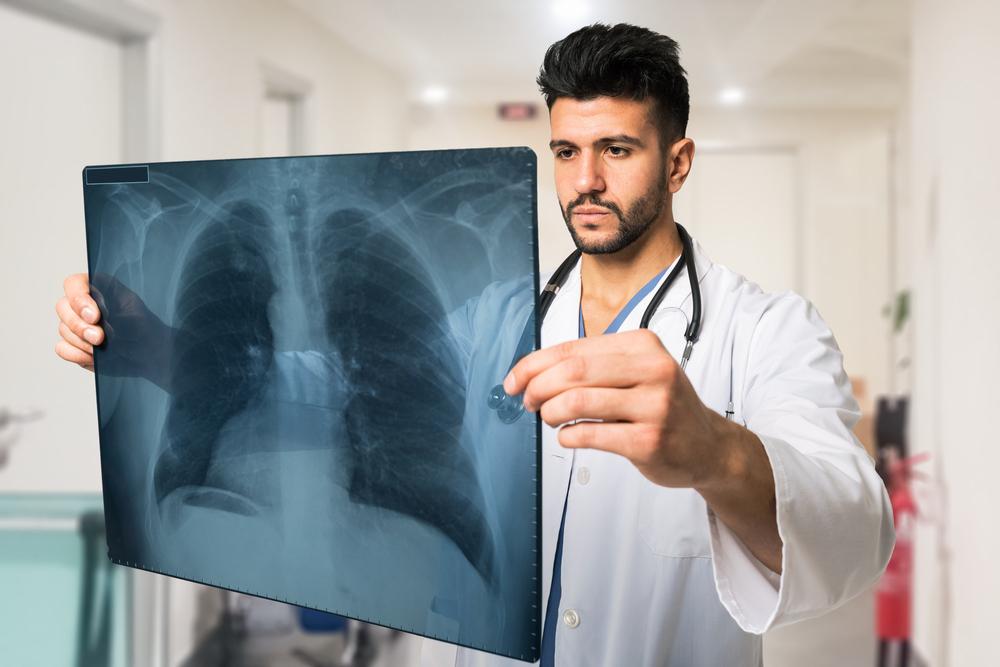
Everything you need to know about lung cancer
Lung cancer can be described as a type of cancer that begins in the lungs of a person. Cancer is a condition which causes mutations in otherwise healthy cells. This causes the cells in the lungs to divide rapidly, leading to the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in both or one of the lungs.
Typically, normal cells are programmed to die at a certain stage in its life cycle, in order to avoid overgrowth. But these mutated cells override that instruction, leading to rapid growth of abnormal cells. These cells do not carry out the regular functions of the healthy cells and start to form tumors, impairing the functioning of the lungs. These tumors reduce the person’s ability to breathe efficiently, thus resulting in providing less oxygen to the entire body via the blood.
The lungs are a pair of spongy organs located in the chest, which helps to take in oxygen when you inhale and then release carbon dioxide when you exhale. It is essential to note that lung cancer is the leading cause of deaths due to cancer in the country among both men and women as per the Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Like any other cancers and diseases, anyone can develop lung cancer, although there are certain risk factors which significantly increase a person’s chance of contracting the condition, like cigarette smoking and constant exposure to secondhand smoking. Nearly 87% of all lung cancer cases are smoking-related in the United States of America. But lung cancer can also occur in a person who has never smoked or experienced secondhand smoking. Other causes of lung cancer are:
- Having a family history of lung cancer.
- Being exposed to carcinogens such as asbestos in the workspace and other harmful environmental substances that are known to cause cancer i.e. arsenic, uranium, chromium, nickel, gasoline exhaust.
- Tuberculosis is also known to cause scarring of the lung tissue which increases the likelihood of developing lung cancer.
- Exposure to high levels of radon gas.
- Exposure to radiation in the chest area through X-rays.
- Pollution in the air that contains trace amounts of coal and diesel exhaust.
Apart from the above, lung cancer can cause many painful complications, which include:
- Difficulty in breathing or shortness of breath. As lung cancer can lead to fluids accumulating around the lungs, it makes it harder for the lungs to fully expand and contract.
- Coughing blood due to bleeding in the airway.
- Pain, especially in patients with advanced lung cancer.
- An excess build-up of fluids in the chest, leading to pleural effusion.
- Metastasis
Although lung cancer has a range of cause and complications, some simple preventive measures can go a long way in reducing the risk of contracting this:
- Not smoking.
- Not being exposed to secondhand or passive smoking.
- Taking precautionary measures to avoid carcinogens at work.
- By eating a diet full of fruits and vegetables and exercising regularly.


